This morning, the Gander Airport Historical Society shared a tweet that I retweeted and started a discussion on Coca Cola, the Second World War, the United States, and advertising. During the discussion, James D Kightly shared a short article he wrote about the Coke advertising during the war, and I mentioned I had done a presentation about it some time ago. So, I am sharing that presentation with you now.
From a US magazine Coke AD in the 40's, showing US servicemen visiting a fishing village near their Nfld base, sharing a refreshment. There were 5 US air bases in NL during the 40, 50, & 60's. Goose Bay, Stephenville, Gander, Argentia & St. John's. 🇺🇦 pic.twitter.com/g7GFsXCToG
— GAHS (@GahsYQX) June 2, 2023

Have a “Coke” = How are things goin’?: North American Soda at the Globe Theatre
By Lisa M. Daly
Prepared for the Stuart Brown Lecture Series, 2013
(note, I don’t believe this lecture series went very far, there may have only been a couple of lectures, and, to be honest, there were only two people at this one, and one of them was my mother! As well, as this was only supposed to be a presentation, there is no bibliography)

In 1935, surveyors Vatcher and Hall determined that Hattie’s Camp, at milepost 213 along the Newfoundland Railway line was an ideal location for an airport. The land was flat and relatively fog free, both a rarity for the island. Such an airport would make mail delivery faster. Aircraft could take off from ships, allowing for mail delivery days earlier.

Soon after construction started and on January 11, 1938, the first aircraft, Fox Moth VO-ADE flown by Captain Douglas Fraser, landed at the airport.

With the advent of World War II, the airport took on a greater importance and construction efforts accelerated. On November10, 1940, an experiment was undertaken to see if flying, or ferrying, of aircraft from North American factories to the European war effort was possible. Seven Hudson aircraft, fitted with extra fuel tanks, under the supervision of Captain Donald C. T. Bennett, took off from the Gander airfield. The flight would have been deemed successful if three of the seven aircraft were safely delivered. Under Bennett’s guidance, all seven aircraft landed in Scotland the following day thus creating the Atlantic Ferrying Organization, which later became the Royal Air Force Ferry Command and ended the war as the United States Army Air Force Transport Command.

Gander’s second role during the war was as a base for Eastern Air Command. This was part of a joint Royal Canadian Air Force and USAAF effort to add an aerial patrol to convoys, and, to a lesser extent, hunt U-boats in North Atlantic waters. All of this war activity meant that what was to be an airport meant to allow for faster mail delivery became the largest airport in the world, one that saw thousands of aircraft pass through and saw a joint effort between the RAF, USAAF and RCAF in the name of fighting the war.
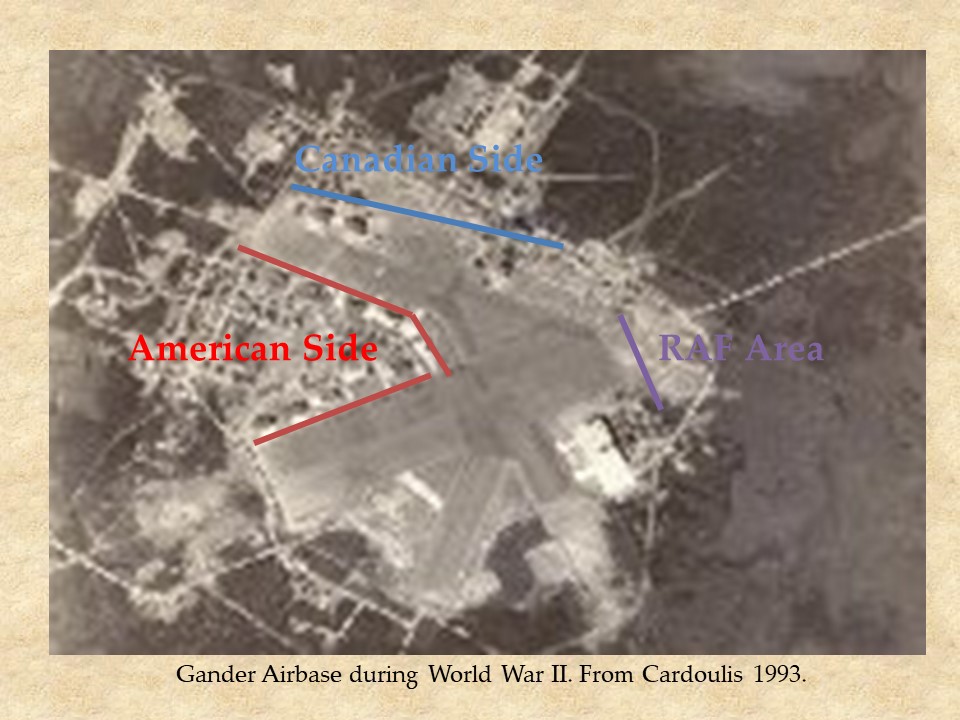
Large numbers of Canadian and American servicemen and women lived at Gander, first known only as the Newfoundland Airport, its exact location kept secret, and Newfoundlanders worked building and maintaining the airport. Gander, unlike any other base in Newfoundland, was not built next to a community, and entry to and from the area could be controlled. Only those with business in the area were permitted to get off the train at Gander. Therefore, was available at Gander had to be specifically brought in for base personnel.
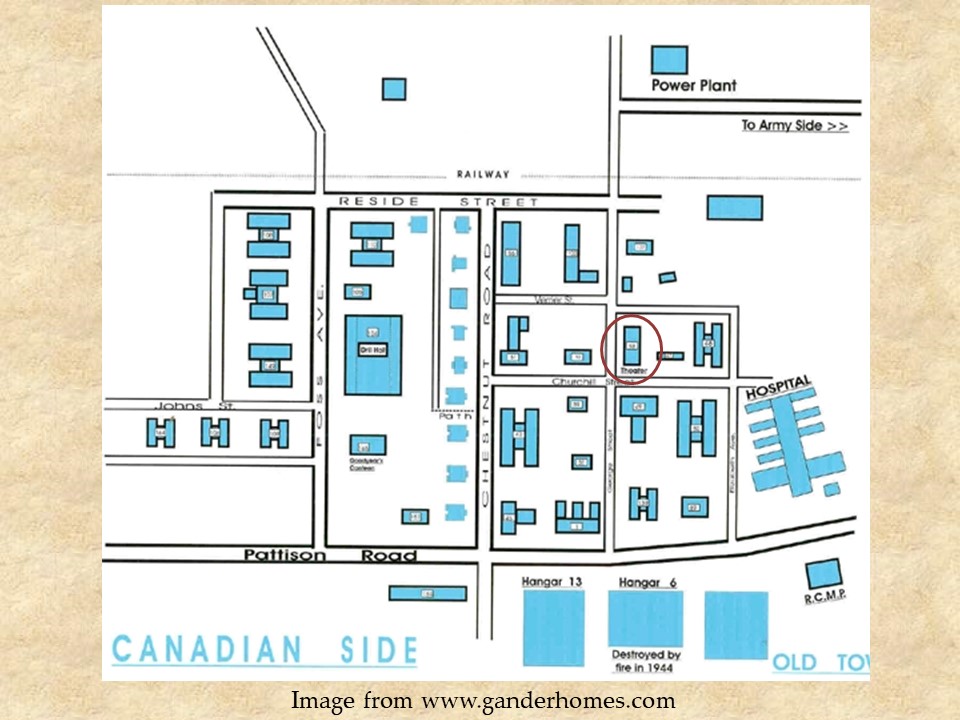
The Globe Theatre was the theatre on the RCAF side of Gander. This area was closer to the railway station than to the runways. The American Side of the base hugged the runway, and was all destroyed after the war. The RCAF side of the base was in use up to the early 1960s, with documents suggesting that the last building to be used in the area was the Sir Frederick Banting Hospital, which was abandoned for the James Paton Memorial Hospital now located on the Trans-Canada Highway near what is currently called the town of Gander. The Globe Theatre had a short life, with an estimated use from 1942 to 1962, and screened movies and performances such as variety shows, base glee clubs, traveling musical and comedy acts, and bands, both local and traveling. Going to the theatre was a favourite activity of GIs, as it was a great place to bring WDs (the women’s division) and visiting women from Grand Falls for a date night. Newfoundlanders were allowed to go to the theatre on certain nights, and children were given access. If it could be timed right, children could catch a show at the Globe Theatre and then run across the base to catch a different movie at the Star Theatre on the American side.

Excavations were undertaken at the Globe in the summer of 2011. The site was chosen because, in contrast to the aircraft crash sites examined for the rest of this project, the Globe was a happy place, a way to escape the hardship and tragedy of war, at least for a short time. Plus, it is one of the areas where there could be more interactions between Newfoundlanders, Canadians and Americans, potentially revealing an exchange of goods between the different countries. Coupled with that, much of the land surrounding the Gander Airport has been contaminated due to improper disposal of hazardous materials after the war. While Transport Canada has cleaned up the area so that it is safe, digging would upset monitoring probes and could potentially unearth hazards. The Globe was in the residential part of the Canadian side, and was one of the few areas determined by Transport Canada to be safe for excavation.

Some foundations were visible on the surface of the site, so, at the suggestions of my supervisor, Dr. Michael Deal, the team worked to uncover the outline of the building. This team consisted of MA student, Eric Guiry and a variety of volunteers, including Kathleen Ellwood, Shannon Green, Chelsee Arbour, Maryanne Baird, Matthew Brake, and of course, Mike Deal. At our busiest day, we had five people working on the site for two days, but usually the team consisted of Eric, Kathleen and myself.

Over 10 non consecutive days we uncovered the foundations of the building, focusing mainly on the exterior foundation, and opened six excavation units. Originally, the plan had been to excavate four units at the entrance to the building, three in the approximate center and one on a rear interior foundation. This unit had a high number of surface finds, including an aluminium tank cover, but excavations revealed little more than the rest of the foundations. This excavation plan was a little too ambitious for the number of excavators available, and only 6 of the 8 units were opened and excavated. During excavation of the foundations and the units, most glass was placed in bags designated to the day, excavator and location on the site. Much of the glass recovered was non diagnostic clear bottle and window glass. Any pieces of interest, involving patterns, logos, bases, etc., found on the foundations were marked and measured in with the surveyor’s level from the site datum; those from the excavation units measured from the unit datum.

Of the glass found on site, most was window glass covered in black paint. While I have not been able to find any pictures of the exterior of the Globe, all buildings on site supposedly looked the same. Therefore, there would have been windows in all of the social buildings, which would have been blacked out for the purpose of the theatre.

A fragment of mirror glass was also found near the rear exterior foundation. A surface find of porcelain, most likely from a toilet, and a decorative cabinet handle were found in this general area. These artifacts and personal recollections from Peter Hoyles, a frequent site visitor who used to attend the Globe just after the war, indicated that the stage was at the rear of the building and the washrooms where located under the stage.

Bottle glass was found throughout the site. Most pieces were clear or green, unidentifiable glass. But, other pieces reflect the countries that were in Gander during the war. Keep in mind, the theatre was in use until the early 1960s, so the glass found is not just reflective of the war period but also the immediate post-war era. Both the Star and Globe Theatres were operational for a time after the war, and many who were children during and after the war remember frequenting both up until the Star was bulldozed and the Globe shut down when the new theater opened in Gander.

There were sodas and aerated waters being sold in Newfoundland at the time, one of the most common companies being Gaden’s Aerated Waters Company, Limited (the name shortened to Gaden’s, Limited in 1942. Gaden’s bottled Keep Kool drinks, which included lemonade, soda water, ginger ale, champagne cider, and nectar drinks when they first opened. Gaden’s opened on Duckworth Street in St. John’s in 1889, and moved to Water Street in 1942 and remained there until it closed in 1977.

Gaden seemed to be popular drinks in Newfoundland, with beers (sort of flavoured sodas) being very popular, to the point where Dominick DeAntonio, a GI who arrived on the Edmund B. Alexander (the ship which brought the first American troops to St. John’s) could no buy pop at a St. John’s restaurant, as the waitress informed him they only sold beers, cherry, grape or orange. A Gaden bottle fragment was actually one of the first diagnostic bottle pieces to be found on site. A piece reading “NEWFOUND(?) This bottle/ of Gaden/ Deposit/ Refi (?)” was found toward the rear of the building. It was unfamiliar to all excavating that day, so Dr. Deal took an image of it back to St. John’s to try to identify it. My mother, on the other hand, grew up in Newfoundland and recognized it right away. This shows that Newfoundlanders were bringing their own favourite beverages to Gander, to the point where it was available at the theatre. Keep in mind, Gander could only be accessed with permission, so unlike other bases in Newfoundland, products could not move in and out of Gander so easily.

Another fragment indicating the presence of Newfoundland products is a green bottle base which features a D inside a diamond. This is actually from a Canadian bottle manufacturer, Dominion Glass Company, Limited, but was used in Newfoundland. There were no bottle manufacturers in the colony, so all soda bottles were imported. While I did determine this was a Canadian made bottle used by a Newfoundland drink company, I could not determine which one.

The most common bottle fragment found on a site belonged to Coke bottles. Shortly after Pearl Harbor, Robert Woodruff, the then president of the Coca-Cola Company, ordered that “We will see that every man in uniform gets a bottle of Coca-Cola for five cents, wherever he is whatever it costs our company.” And the cost was to be the same for all American men in uniform; five cents a bottle. If Americans were attending the Globe, Coke would have cost five cents, but, the Canadian side was subject to different duty prices (meaning Canadian supplies were subject to duty whereas the American goods were all duty free) so it is conceivable that the price was different on either side of the runway. To provide Coke to the men in uniform, and because shipping bottles of Coke took up too much space needed for weapons and war supplies, Coke began building factories around the world and would ship only the syrup needed to produce the drink. But, Coca-Cola was already being bottled in Newfoundland. In 1938, Gaden’s began bottling Coke, and continued to do so until the facility closed in 1977.

One of the reasons why Coke dominates the assemblage is the iconic Coca-Cola bottle. The green glass and the curved bottle are trademarked to the Coca-Cola Company, so any of the light green glass, or clear glass with the ridged curve is known to be part of a Coke bottle. No other soda has such a distinct bottle, most being identified only if part of the logo is found. In other cases, such as a cross hatching pattern seen on a fragment, the piece could belong to multiple types of sodas made by a single company.
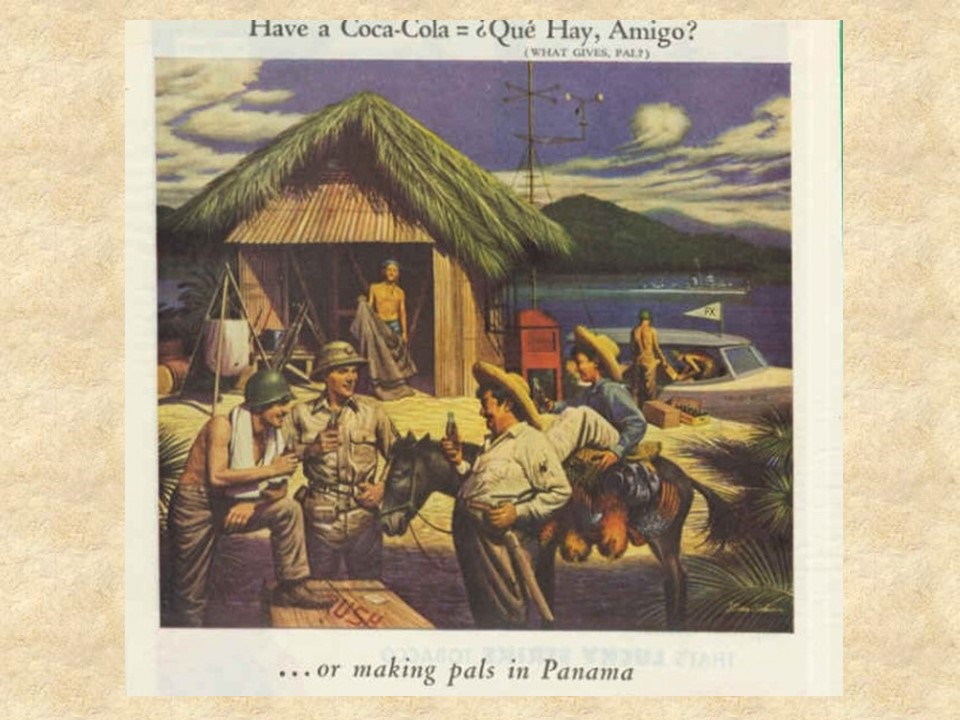
World War II saw Coca Cola spread all over the world, and Coke used this as an advertising tool in the United States. Advertisements depicted servicemen and women in all of the exotic locations sharing Coke with the local populations in places such as Alaska, China, Iceland, New Zealand, the Admiralty Isles, Brussels, Panama, and of course, the fishermen of Newfoundland.









The history of Pepsi-Cola in Newfoundland is a little more difficult to piece together. Pepsi was a registered trademark in Canada in 1906, the first bottling facility outside of the United States opened in Montreal in 1934. This obviously does not mean that Pepsi was available in Newfoundland at that time. A Pepsi franchise was obtained in 1944 by Reginald C. Harvey of Browning-Harvey Limited, and this was the first instance of Pepsi being bottled in Newfoundland. I could not determine if Pepsi was regularly shipped in to Newfoundland at any time before this date.

The style of the Pepsi-Cola bottle changed within a few years of the end of the war. During the war, Pepsi had a sort of cross-hatch design with the words “Pepsi Cola” embossed on the glass. A fragment of this was found at the Globe, identified by the pattern and the LA in cola. The Pepsi-Cola logo is not as easy to date, as although the bottle changed slightly after the war, the Pepsi-Cola logo remained the same.

Finally, this piece is potentially, but not confirmed, to be part of a Canada Dry bottle. Canada Dry began manufacture in 1890 as a dry ginger beer, something less sweet than others on the market. It was popular in Canada, and it would be unlikely for it to not have been present in Gander. But, the presence of Canada Dry at the Globe cannot be stated for certain.
As previously mentioned, much of the bottle glass found on site could not be positively identified. There was a large amount of unmarked clear and green glass excavated, but without distinct markings or logos it is not possible to know one bottle from another as many bottles used by different companies and coming from different manufacturers were of similar styles. For instance, Gaden’s ginger beer was marketed in emerald green bottles, but none of the green bottle glass found had the distinctive Gaden’s trademark of a sea-lion on an ice-pan.

A major problem with framing this research within the timeframe of the Second World War is that the theatre was in use after the war. Evidence of this is seen in the presence of soda cans which were not available until after the war. Coca-Cola began putting Coke in cans in 1955, but took a few years to determine how to make a liner that would not alter the taste of the drink. Coke in cans was available for mass distribution in 1959. The slight markings on the lower can are similar to the can shown; a design available in 1961. Again, an exact date for the closing of the Globe could not be found, but the residents and services of the Canadian side of the base were transferred to what is now Gander starting in 1950, mostly completed by 1957, and the hospital, believed to be the last building transferred, closed in 1964. In 1957, many of the more specialized buildings were still in the old town area, such as the post office and the library, and as the library was next to the theatre, it is assumed the Globe was still in the old town. Therefore, given the evidence of the drink cans coupled with the documentary evidence, it is believed that the Globe closed in the early 1960s.

One last bottle of interest is that of a complete Gordon’s Gin bottle found a half meter below the surface, near the entrance to the building. There is no other indication of alcohol available on site, and during the war, if the regulations were the same as the USAAF theatre, the Star, alcohol was not permitted on site. Therefore, speculation can lead to ideas that this bottle may have belonged to a projectionist, as it was in an area close to the pieces of the projector and film fragments, or perhaps some liquid fortification for a performer before a show, or, more likely, one of the servicemen or women looking for courage before getting on stage in front of their peers to perform in a variety show or a glee club performance.

As usual, I cannot thank the people involved in this project enough. I had so many great workers and volunteers who without whom I might still be wandering the woods or lost in a bog in Gander. And to Mike for all of his help, hopefully we can get this thesis finished quickly and I’ll be out of your hair, at least until another interesting plane crash project comes up. And to all of the companies, groups and offices that provided financial and logistical support, access to sites, and for helping me locate sites and sharing historical records, it is all so very appreciated.











